Are you considering adopting a Lean Startup approach for your business but unsure if it’s the right fit? Embarking on such a journey can be daunting, especially when it involves adopting new principles and methodologies for your business operations.
Lean Startup: Is It Right For You? In a nutshell, the Lean Startup approach is right for you if your business can thrive on fast iteration, customer feedback, adaptability to change, and an emphasis on continuous learning. Key principles of Lean Startup, such as Minimum Viable Product (MVP) development and pivoting or persevering, can make a significant impact on your business if correctly implemented.
Now that you have a basic understanding, we invite you to dive deeper into this blog post to explore the core principles, benefits, and challenges of the Lean Startup methodology. Learn how to evaluate its compatibility with your business and grasp crucial considerations to make an informed decision about adopting this innovative approach.
Understanding Lean Startup
Definition and Origins of Lean Startup
The Lean Startup methodology is a business approach that stems from the concept of lean manufacturing, focusing on efficiency and eliminating waste. The Lean Startup methodology was introduced by entrepreneur and author Eric Ries, who outlined this framework in his influential book, “The Lean Startup” published in 2011.
This innovative methodology aims at developing and launching new products or services in the most rapid and efficient way possible. The core idea behind the Lean Startup is that startup businesses must continually adapt and learn in order to succeed in today’s ever-changing business landscape. A startup has to validate and iterate its business model based on real customer feedback, resulting in a faster and more efficient path to market.
Key Principles of Lean Startup
There are three key principles of Lean Startup that function as its foundation, guiding businesses in navigating the uncharted waters of entrepreneurship:
- Fast iteration: The Lean Startup methodology emphasizes speed in the development process, allowing businesses to build, measure, and learn from their efforts quickly. This short feedback loop ensures that you are developing products or services that cater to your target audience’s needs and allows for quick adjustments and improvements as required.
- Customer feedback: Listening to what your customers have to say is essential for adapting your product or service to meet their needs. Continuous feedback from customers, both current and potential, helps you refine your offering and uncover potentially overlooked opportunities.
- Build-Measure-Learn: This principle represents the iterative cycle followed by Lean Startups. It involves building a Minimum Viable Product (MVP), measuring customer response and learning from it, and using collected data to either improve the product or pivot the business model. This cycle, based on rapid experimentation, is designed to drive a continuous process of learning and adaptation.
According to the Harvard Business Review, “Lean startups begin by searching for a business model. They test, revise, and discard hypotheses, continually gathering customer feedback and rapidly iterating on and reengineering their products.”
The Role of MVP (Minimum Viable Product) in Lean Startup
A Minimum Viable Product (MVP) is a fundamental concept in the Lean Startup methodology. It represents the simplest, most basic version of your product or service that is still functional and valuable to customers.
The purpose of an MVP is to test your value proposition in the market quickly, gather customer feedback, and guide you in modifying or improving your product. Developing an MVP allows you to learn as much as possible about your target audience’s needs while investing the least amount of time, effort, and capital.
The MVP approach encourages startups to release a product that meets the minimum requirements to solve a problem for early adopters. As you gather feedback from these users, you can iterate and refine the product to better suit the market needs, ensuring that your final offering is a result of thorough market testing rather than guesswork.
Pivoting or Persevering: When to Make the Call
While implementing the principles of Lean Startup, businesses follow the Build-Measure-Learn cycle to test and validate their hypotheses. The results of this process will often lead to a crucial decision – whether to pivot or persevere.
Pivoting refers to significantly altering your business model or product offering based on the customer feedback and learnings gathered from the MVP testing. Pivoting helps businesses explore new market opportunities, address specific customer pain points more effectively, or create a more sustainable growth path. Failure to pivot when necessary can lead to a startup spending valuable time and resources on a product that does not meet the market’s needs.
Persevering is the decision to keep pursuing your existing business strategy with minor adjustments, based on the belief that the current model is fundamentally sound. This decision generally follows positive customer feedback, validation of the business hypothesis, or promising results after several cycles of iteration.
Deciding when to pivot or persevere is crucial for startups because it can determine the trajectory of their growth. It’s essential to base the decision on accurate data, market research, and customer feedback rather than intuition or personal preference.
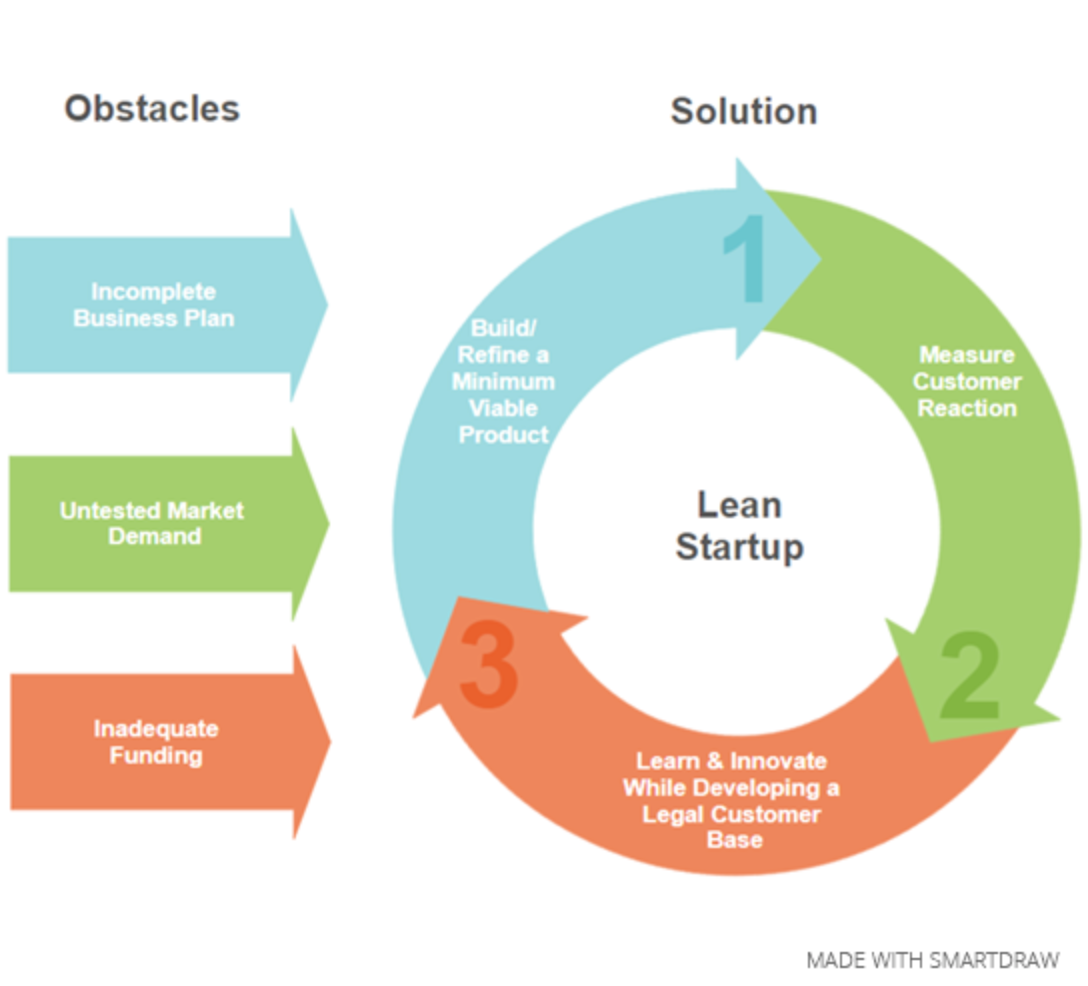
Source: The Lean Startup
As you delve deeper into the principles and practices of Lean Startup, you’ll gain a better understanding of how these concepts fit within your organization and support your entrepreneurial venture’s success. Fast iteration, customer feedback, and the development of MVPs help startups navigate the foundational stages of their business, leading to informed decisions on pivoting or persevering. As you embrace these principles and methodologies, you’re on your way to maximizing the odds of success for your startup.
Assessing Your Business Idea Against Lean Startup Compatibility
Before diving head-first into the Lean Startup methodology, it’s crucial to evaluate whether your business idea aligns with this approach. Some crucial factors to consider include the following:
- Type of Product/Service: If you’re offering a highly innovative solution that caters to a niche market, the Lean Startup methodology may be beneficial for fast iterations and gathering customer feedback.
- Market Maturity: When targeting a developed, saturated market, the Lean Startup approach could pose challenges when it comes to differentiation. On the other hand, a nascent market presents a fruitful opportunity for Lean startups.
- Customer Personas: To apply the Lean Startup approach, you need to have customers willing to engage in constant feedback and iteration. If your target market is open to experimentation and adapts quickly to changes, Lean Startup might be suitable.
It’s essential to weigh these factors before committing to the Lean Startup approach to avoid potential pitfalls and wasted resources.
Understanding the Marketplace and Customer Needs
In the world of Lean Startups, market research and customer feedback are paramount when it comes to identifying and meeting customer needs. Constant feedback-driven iterations enable startups to tailor their products and services to what customers truly want.
One effective method of capturing customer feedback is customer interviews. These interviews offer valuable insights into customers’ preferences, pain points, and expectations. Additionally, startups can use:
- Surveys
- Usability testing
- Analytics tools
These methods contribute to a comprehensive understanding of the marketplace and enable Lean startups to create products and services that cater to their customers’ unmet needs.
Lean Startup Success Stories
Countless startups have achieved success by following Lean principles. A few notable examples include:
- Dropbox: Utilizing the Minimum Viable Product (MVP) approach, Dropbox launched a simple video demo which showcased their file-sharing functionality. Gathering feedback and building upon their MVP allowed them to dominate file storage and sharing.
- Airbnb: Starting as a simple website to rent out spare rooms, Airbnb integrated user feedback consistently, leading to an exceptional user experience that eventually disrupted the hotel industry.
- Zappos: Before becoming a giant in online retail, Zappos tested the market with a basic website. By listening to customers and iterating on their process, Zappos refined their offerings and grew into the e-commerce powerhouse it is today.
These examples emphasize the power of Lean Startup principles in shaping companies with winning products and services.
Potential Downsides and Criticisms of Lean Startup
Despite its numerous success stories, the Lean Startup approach faces certain criticisms and potential downsides. Some of these include:
- Market Saturation of Lean Startups: With numerous startups following the Lean methodology, markets may face saturation with similar or competing products. This makes it difficult for individual innovators to differentiate themselves, as suggested by the high rate of startup failure.
- Possibility of Rushed Releases: The mantra of “release early, release often” is central to Lean Startup’s MVP approach. However, this can sometimes lead to rushed releases, resulting in products that lack quality or have glaring defects.
While these criticisms are worth considering, it’s essential to remember that success depends on the effective implementation of Lean Startup principles and can vary from one company to another.
Agile Development vs. Lean Startup Methodologies
Both Agile Development and Lean Startup are popular methodologies adopted by startups, but how do they differ, and which one is right for your organization?
Agile Development emphasizes the iterative development of products, with continuous collaboration among team members across different functions. This approach focuses on flexibility and adaptability to changing market conditions.
Lean Startup, on the other hand, revolves around the MVP, customer feedback, and the Build-Measure-Learn loop. This approach is geared towards efficiently finding a sustainable business model by iterating quickly and, when necessary, pivoting.
Both methodologies prioritize adaptability, but they differ in focus. While Agile Development zeroes in on product development, Lean Startup is broader, considering the entire business model.
When deciding which methodology is suitable for your organization, consider factors like product complexity, target market maturity, and your team’s capacity to adapt to change.
Financial Implications: Can You Afford the Iterative Cycles of Lean Startup?
The iterative cycles of the Lean Startup approach require a continuous investment of resources to facilitate the releases and feedback loops. Budget constraints and risk tolerance are essential factors to consider when evaluating the feasibility of a Lean Startup.
To embrace the Lean methodology, an organization should have:
- Sufficient runway: Adequate funding to support the cycles of product releases, feedback-gathering, learning, and iteration.
- Risk tolerance: A willingness to invest in iterations and pivots, especially when a significant change in the business model requires additional resources.
Organizations that cannot afford these cycles or do not have adequate risk tolerance may want to reconsider their approach.
The Role of Your Team: Does Your Team Have the Discipline and Culture for Lean Startup?
A crucial aspect of a successful Lean Startup is the ability to quickly adapt and implement feedback. As such, your team’s discipline and culture play a significant role in determining the suitability of this approach. Key considerations include:
- Adaptability: Your team must be open to change and learning from mistakes while maintaining a mindset of continuous improvement.
- Discipline: Implementing the Build-Measure-Learn loop and pivoting efficiently requires discipline and dedication to the process.
- Collaborative work culture: A culture of collaboration promotes open communication and information-sharing, making it easier to identify and address issues as they arise.
In conclusion, considering your organization’s compatibility with Lean Startup principles is vital to the success and effectiveness of this approach. Evaluate the key deciding factors, such as your business model fit, capacity for measuring progress, adapting quickly, market demand, and team culture, to make an informed decision on adopting the Lean Startup methodology for your venture.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Lean Startup?
Lean Startup is an innovative approach to entrepreneurship that emphasizes the use of rapid iterations, customer feedback, and minimum viable products (MVPs) to learn and adapt to the market quickly. It facilitates the development of a sustainable and profitable business model through continuous experimentation and learning.
How is the Lean Startup approach different from Agile Development?
While both methodologies prioritize adaptability, Agile Development focuses on the product development process through iterative collaboration among team members. Lean Startup, in contrast, encompasses the entire business model, emphasizing the MVP, customer feedback, learning, and pivoting when necessary.
Why is customer feedback important in Lean Startup?
Customer feedback is crucial in the Lean Startup approach as it provides startups with valuable insights into customers’ needs, preferences, and pain points. This feedback informs iteration cycles, enabling startups to refine their products and services quickly to cater to the evolving market demands.
Is Lean Startup ideal for every type of business?
Not necessarily. Lean Startup is better suited for businesses offering innovative products or services in niche or emerging markets. Additionally, adopting Lean Startup requires a team with an adaptable and disciplined culture, adequate financial resources, and a willingness to accept the risks associated with continuous iteration.
What are the downsides and criticisms of the Lean Startup approach?
Some of the criticisms and potential downsides of the Lean Startup approach include market saturation of similar lean startups, making it difficult for companies to differentiate themselves, and the possibility of rushed product releases, which could result in lower quality or glaring defects. However, these downsides can be mitigated by effectively implementing the Lean principles.